Ngrok and Postman
In this topic, we demonstrate a way to share our localhost server with anyone and anywhere by using ngrok and postman to create a secured tunnel to our localhost.
Table of contents
Before we start, you need to have installed ngrok and postman.
Ngrok
The ngrok is used to connect into secured behind our firewall. It is easy to use and does not need to set up forwarding and change the network. In our localhost, it runs thru our client server and ngrok run thru a secured tunnel.
To check if there’s installed ngrok run in the terminal ngrok -v.
Register to Ngrok
After we install the ngrok. Register here.
After registration, login your account and go to Setup & Installation and copy your ngrok config.
Go to your terminal and paste your ngrok config.
$~/KodaCamp> ngrok config add-authtoken XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX_XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Authtoken saved to configuration file: /Users/kodacamp/Library/Application Support/ngrok/ngrok.yml
Now, your authenticate token is saved.
To start the HTTP tunnel forwarding to our local port 3000, run this ngrok http 3000 in your terminal.
$~/KodaCamp> ngrok http 3000
This command sets up a tunnel between the application and the HTTP server on 3000 (local port).
ngrok (Ctrl+C to quit)
Join us in the ngrok community @ https://ngrok.com/slack
Session Status online
Account xxxxxxxx@gmail.com (Plan: Free)
Update update available (version 3.1.1, Ctrl-U to update)
Version 3.1.0
Region Asia Pacific (ap)
Latency 28ms
Web Interface http://127.0.0.1:4040
Forwarding https://f39a-103-43-215-138.ap.ngrok.io -> http://localhost:3000
Connections ttl opn rt1 rt5 p50 p90
7 0 0.00 0.00 20.35 24.02
All the details are now shown. In the forwarding, the localhost turns to ngrok which means we can access the localhost thru ngrok with a encrypted tunnel.
Connect your project
Copy your ngrok hostname and paste it to your browser.
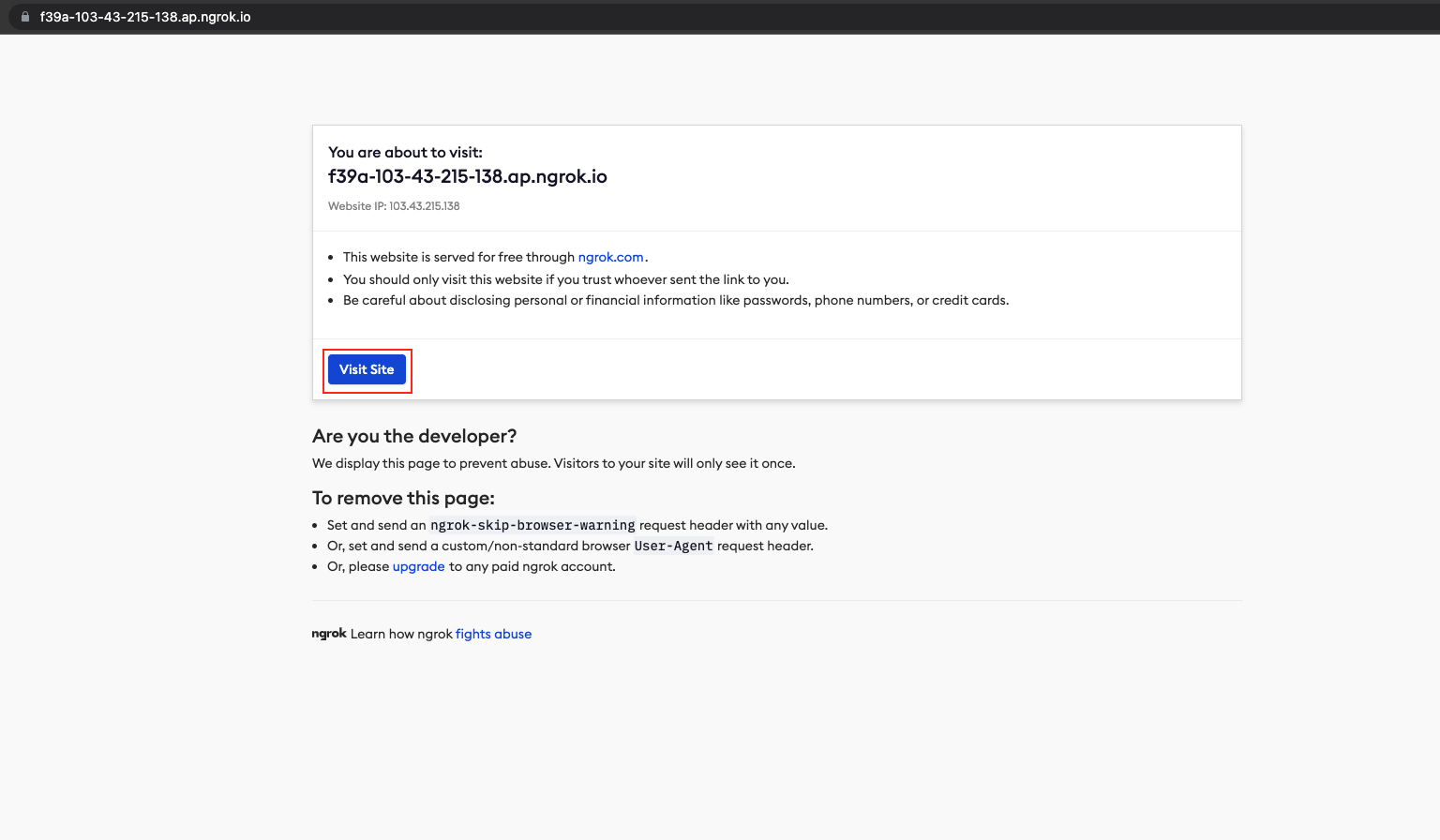
Click Visit Site and there will be an error because the hostname it’s not configured.
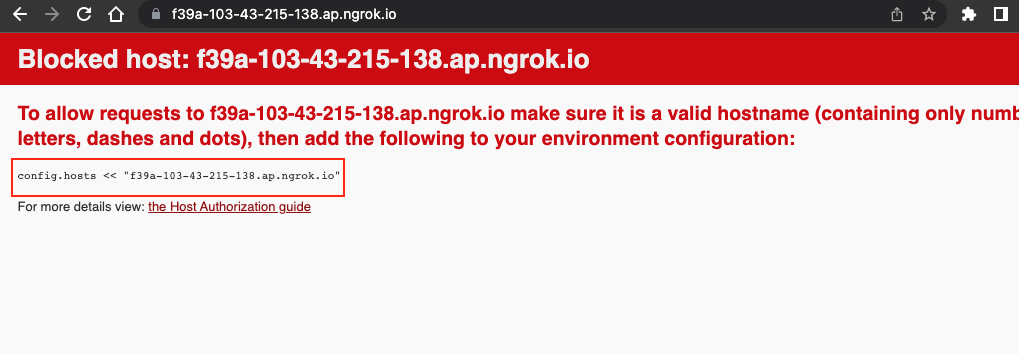
Our hostname is invalid we need to configure our hostname in development.rb under the config/environments.
# config/environments/development.rb
# ...
config.hosts << "admin.com"
+ config.hosts << "f39a-103-43-215-138.ap.ngrok.io"
# ...
Once you add or modify the config you need to restart server for changes.
Back to your browser and refresh. Redirect to f39a-103-43-215-138.ap.ngrok.io/api/regions.
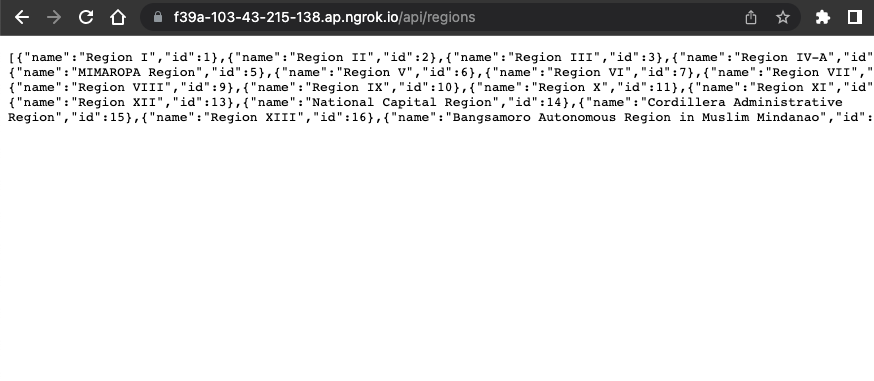
As you can see its hard to read the data, you can install JSON Formatter extension in your chrome to make your data easily to read. The JSON Formatter is only available in chrome.
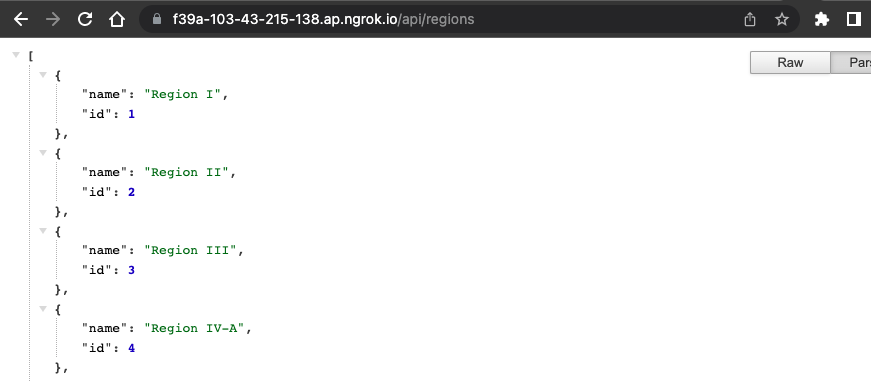
The JSON Formatter help us to make the string of the data more readable.
The ngrok now is working and the requests are a success, you can run your application by using ngrok on any device as long as the ngrok is running on your terminal. Once your ngrok is close you need to start HTTP forwarding and add a hostname to your config again to run.
Postman
The postman is an API platform to build and is an application used for API testing it helps us to build and test.
We will test the created ngrok in our postman, First, create a HTTP request.
Creating Requests
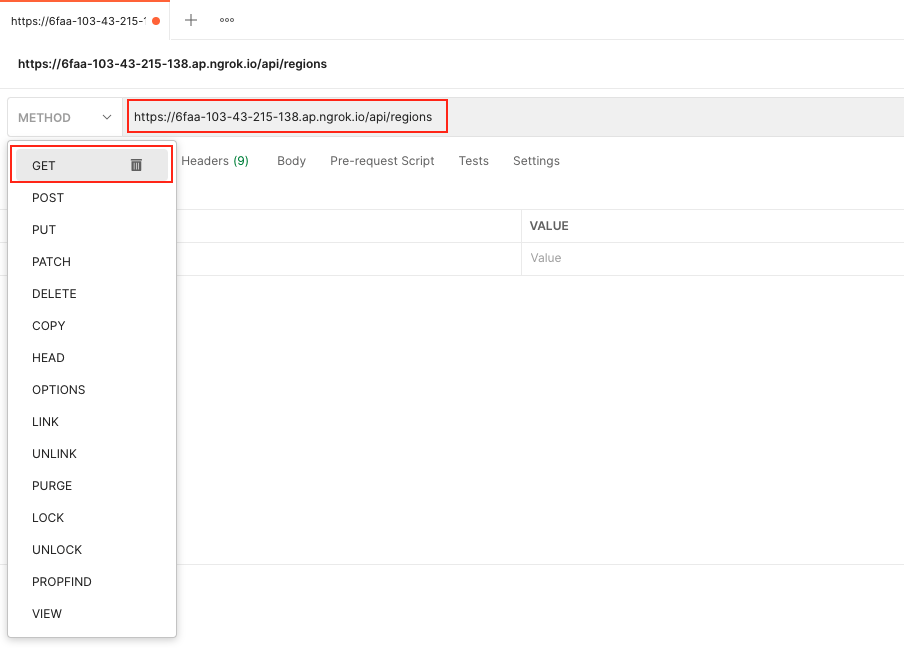
Setting request URL Every request you send to
postmanrequires a URL it represents to our API. Enter your urlhttps://your_host.ngrok.io/api/regions/.Selecting request method
GETretrieving dataPOSTadd dataPUTandPATCHupdate existing dataDELETEdelete existing data
You can change your method depending on API. The only request for the PSGC API is a get request.
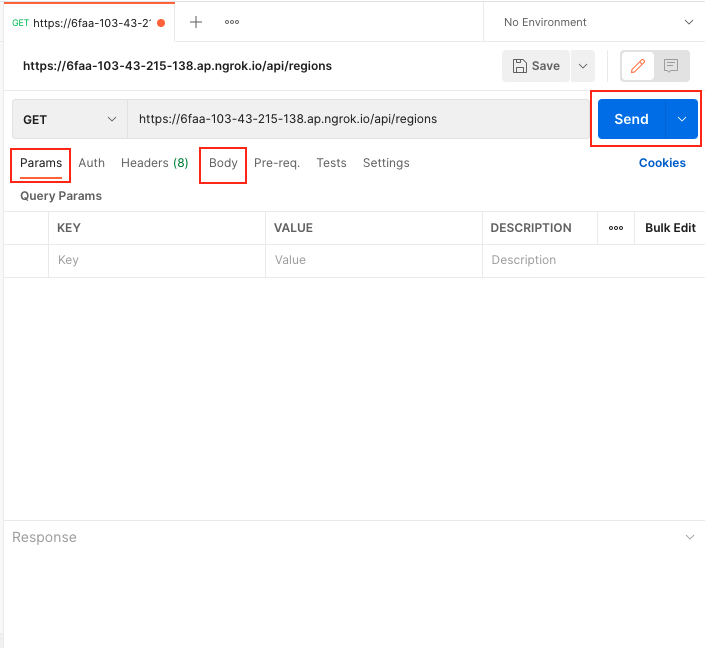
Sending parameters and body data
Sending Parameters
You can send parameters using in Params tab or you can append them at the end of the URL. There are two types of parameters the query and path parameters. The query parameter is used to filter the data in the API, and the path parameter used to select specific data.
Example of the query: /api/regions/get?region_id=1 returns all the data with region_id is 1.
Example of the path: /api/regions/:id and add the value you want to return data.
Sending Body Data
You can send body data using in Body tab with the request if you are adding and updating the data. For example, you want to send a request to add a new barangay to your database. You need to include the details in the JSON.
Once you are done setting up, click Send and check the response.
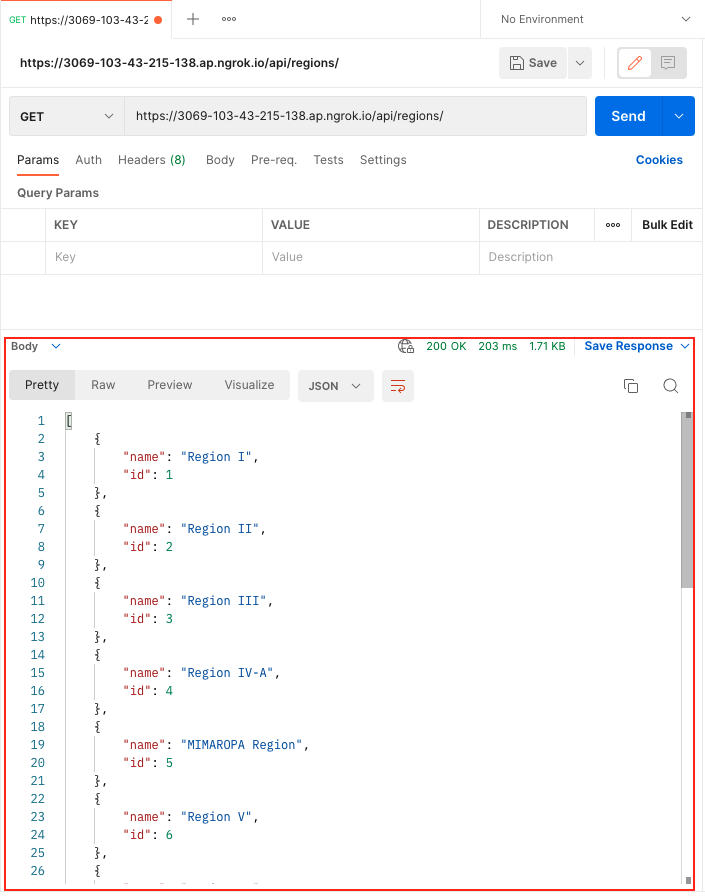
Now, our project successfully runs on a web API server locally by using ngrok and postman.